What is Ventricular Trigeminy? - Definition, ECG, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Three consecutive premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) constitute ventricular trigeminy, a kind of irregular cardiac rhythm. PVCs, or premature ventricular contractions, are contractions of the ventricles that take place before the regular electrical signal is received. This might result in an additional beat or a skipped beat. Ventricular trigeminy may require more testing and care because it can be a sign of a serious heart problem.
Definition
Trigeminy is characterized by a tightening or contraction that occurs over the course of three beats and originates in the ventricles. The extra contractions interfere with the normal pumping sequence because they occur before your next regular heartbeat.
ECG
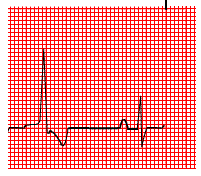
Ventricular trigeminy is commonly identified on an ECG by the occurrence of three consecutive premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), each of which is followed by a normal QRS complex. These PVCs will show up as irregular heartbeats on an electrocardiogram, and they may be differentiated from regular heartbeats by looking at their pattern and frequency.
In addition, if there is any underlying heart illness, it will be revealed by the ECG. Additional cardiac diseases, including myocardial infarction and heart block, can be diagnosed alongside arrhythmias including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, tachycardia, and bradycardia.
Symptoms
Depending on the etiology and severity of the ailment, ventricular trigeminy can manifest in a wide range of symptoms. Some individuals may experience no symptoms, while others may exhibit the following:
- Additional or skipped heartbeats
- Palpitations (a sense of fluttering or pounding heart)
- Discomfort or pain in the chest
- Breathing difficulties
- Feeling faint or unsteady
- Tiredness
- Syncope
Causes
The following are some of the possible causes of ventricular trigeminy:
- Ventricular trigeminy can be caused by coronary artery disease, which occurs when plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries and reduces the blood supply to the heart.
- Dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathies are two examples of cardiomyopathies that can cause ventricular trigeminy.
- Ventricular trigeminy can be caused by an electrolyte imbalance, specifically an abnormality in blood potassium, magnesium, and calcium levels.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs and other medicines can cause ventricular trigeminy as a side effect.
- Both caffeine and alcohol are known to raise heart rate, which in turn can lead to ventricular trigeminy.
- Sometimes the reason for ventricular trigeminy is unknown, and this condition is called "idiopathic."
Treatment
The underlying etiology, the severity of the ailment, and the presence of symptoms all influence the course of treatment for ventricular trigeminy. The following therapy may be necessary for some patients with ventricular trigeminy while not being necessary for others:
Medication: Drugs like beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers can be used to lower heart rate and decrease the frequency of premature ventricular contractions.
Supplements or drugs may be recommended to restore electrolyte balance in patients with ventricular trigeminy caused by an electrolyte imbalance.
Changes in lifestyle, such as giving up tobacco, cutting back on alcohol, and reducing caffeine intake, have been shown to decrease ventricular trigeminy episodes.
Premature ventricular contractions can sometimes be treated by a procedure known as cardiac ablation, which involves destroying a small piece of heart tissue.
If ventricular trigeminy is the result of a more serious heart ailment, like a valve malfunction, surgery to repair or replace the valve may be necessary.
If your disease is not life-threatening, your doctor may suggest coming in for follow-up appointments to monitor your progress.
 Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
January 25, 2023
Rating:
Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
January 25, 2023
Rating:











