Brenner tumor Symptoms, Causes, Pathology, Ultrasound, Treatment
Brenner tumor is the cancer of ovaries. It is the subtype of surface epithelial-stromal tumor. This is the group present in ovarian neoplasm. It is the rare form of tumor reported till now. There are three types of Brenner tumor i.e. benign, malignant and borderline Brenner tumor. The benign Brenner tumor is present in about 6% of cases reported. This can occur in both ovaries. The atypical proliferative tumor is the other name of borderline Brenner tumor. In this the tumor cells are at higher proliferation rate as compared to benign tumor. Malignant Brenner tumor are very rare.
Mostly the Brenner tumor is asymptomatic. Benign Brenner tumor do not cause symptoms most of the time. The main symptom regarding Brenner tumor is the pain in pelvic region i.e. lower abdomen. The Brenner tumor is asymptomatic that’s why it is diagnosed during examination of pelvic region or ultrasound. Brenner tumor lead to other diseases like endometrial adenocarcinoma, vaginal adenocarcinoma, transitional tumor of the bladder. Brenner syndrome also causes the inflammation of endometrium layer and sometimes may cause the heavy bleeding continue after menstrual cycle ends. All these conditions indicate the presence of Brenner tumor in ovaries.
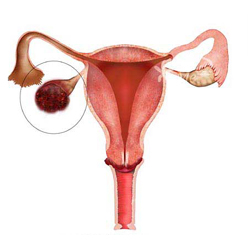
Ultrasound or sonography is the diagnostic tool to diagnose and check the severity of the Brenner tumor. Ultrasound imaging is a painless technique and also easy to perform. Benign brenner tumor are solid and found in almost 50% of cases. Mostly the ultrasound report of benign Brenner tumor mix it with other neoplasmic tumors. Benign Brenner tumor is about 2-6 cm in size. The borderline Brenner tumor are about 9cm in diameter and malignant Brenner tumor is of various sizes along with irregular walls.
The pathological findings found about Brenner tumor are as follows:
The Brenner tumor are about 6% bilateral. And remaining are unilateral along with firm structure. It is white to yellow in color. It has a wide resemblance to the fibroma or thecoma. They appear as solid and cystic nests. Its epithelial outlines are sharp. The tumor cells are uniform, having pale cytoplasm and polygonal in appearance. They are small in size but have distinct nucleus. The tumor is metaplastic along with cystic formation which is prominent in the reports. The tumor have a papillary pattern with proliferation.
The main cause reported behind the formation of Brenner tumor in ovaries is the production of p63 protein. As Brenner tumor is formed along with other tumors present in ovaries. So they are only diagnosed during the lower abdominal examination and during gynecologic surgery. Only the Brenner tumor produces the p63 protein which indicates its presence in patient. So, the protein named p63 is considered the tumor maker only for the Brenner tumor. The type of Brenner tumor i.e. malignant Brenner tumor also do not form the tumor maker protein named p63. This protein is the only cause behind it.
The Brenner tumor when diagnosed it may be at its last stage or starting phase. The age factor and severity is also considered. The treatment option of Brenner tumor is the surgical removal of tumor. The surgery is performed as a treatment to treat the Brenner tumor. The reoccurrence of benign and borderline Brenner tumor is very less or no reoccurrence after surgical removal of tumor. But the case is opposite in the malignant Brenner tumor. There is a high risk of reoccurrence of Brenner tumor after malignant Brenner tumor surgery. Chemotherapy is used after surgical removal of surgery.
Brenner tumor Symptoms
Mostly the Brenner tumor is asymptomatic. Benign Brenner tumor do not cause symptoms most of the time. The main symptom regarding Brenner tumor is the pain in pelvic region i.e. lower abdomen. The Brenner tumor is asymptomatic that’s why it is diagnosed during examination of pelvic region or ultrasound. Brenner tumor lead to other diseases like endometrial adenocarcinoma, vaginal adenocarcinoma, transitional tumor of the bladder. Brenner syndrome also causes the inflammation of endometrium layer and sometimes may cause the heavy bleeding continue after menstrual cycle ends. All these conditions indicate the presence of Brenner tumor in ovaries.

Brenner tumor Ultrasound
Ultrasound or sonography is the diagnostic tool to diagnose and check the severity of the Brenner tumor. Ultrasound imaging is a painless technique and also easy to perform. Benign brenner tumor are solid and found in almost 50% of cases. Mostly the ultrasound report of benign Brenner tumor mix it with other neoplasmic tumors. Benign Brenner tumor is about 2-6 cm in size. The borderline Brenner tumor are about 9cm in diameter and malignant Brenner tumor is of various sizes along with irregular walls.
Brenner tumor Pathology
The pathological findings found about Brenner tumor are as follows:
The Brenner tumor are about 6% bilateral. And remaining are unilateral along with firm structure. It is white to yellow in color. It has a wide resemblance to the fibroma or thecoma. They appear as solid and cystic nests. Its epithelial outlines are sharp. The tumor cells are uniform, having pale cytoplasm and polygonal in appearance. They are small in size but have distinct nucleus. The tumor is metaplastic along with cystic formation which is prominent in the reports. The tumor have a papillary pattern with proliferation.
Brenner tumor Causes
The main cause reported behind the formation of Brenner tumor in ovaries is the production of p63 protein. As Brenner tumor is formed along with other tumors present in ovaries. So they are only diagnosed during the lower abdominal examination and during gynecologic surgery. Only the Brenner tumor produces the p63 protein which indicates its presence in patient. So, the protein named p63 is considered the tumor maker only for the Brenner tumor. The type of Brenner tumor i.e. malignant Brenner tumor also do not form the tumor maker protein named p63. This protein is the only cause behind it.
Brenner tumor Treatment
The Brenner tumor when diagnosed it may be at its last stage or starting phase. The age factor and severity is also considered. The treatment option of Brenner tumor is the surgical removal of tumor. The surgery is performed as a treatment to treat the Brenner tumor. The reoccurrence of benign and borderline Brenner tumor is very less or no reoccurrence after surgical removal of tumor. But the case is opposite in the malignant Brenner tumor. There is a high risk of reoccurrence of Brenner tumor after malignant Brenner tumor surgery. Chemotherapy is used after surgical removal of surgery.
Brenner tumor Symptoms, Causes, Pathology, Ultrasound, Treatment
 Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
July 15, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
July 15, 2017
Rating:
 Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
July 15, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
July 15, 2017
Rating:











