Enterocutaneous fistula Symptoms, Causes, Calssification, Complications, Treatment
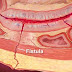
Fistula is the connection between 2 epithelium layers which is not normal. Enterocutaneous fistula is the abnormal connection between the epithelium of the two surfaces these are the skin and the stomach or intestine (small or large). This fistula can generate from duodenum, jejunum, ileum, colon or rectum and make connection with abdominal skin. This fistula can also generate from stomach and esophagus. Due to this abnormal fistula development, the stomach and intestinal contents get leak from body. Even with proper surgical treatment and management with antibiotics and other medicines, the mortality rate regarding this disease is still 10%.

There are many causes behind this fistula formation between intestine and skin. Some of them are as follows:
These are the most common symptoms reported regarding enterocutaneous fistula. But this can also occur secondary to an inappropriate surgery.
The most common symptoms associated with enterocutaneous fistula are as follows:
Enterocutaneous fistula is classified into two main classes
Enterocutaneous fistula is further classified into three groups on the basis of output volume.
Complications associated with enterocutaneous fistula are sepsis, electrolyte abnormalities and malnutrition. The extent of sepsis occurred totally depends upon the condition of enterocutaneous fistula. As if the fistula formed is direct then the sepsis will also less, but if the fistula formed indirectly with skin then the sepsis rate will be high as well. And the patient may become toxic. Patient may feel ill due to excessive loss of nutrients through leakage via fistula opening. This leakage also cause imbalance in the electrolyte concentration which may prove fatal for the patient.

Enterocutaneous fistula Causes
There are many causes behind this fistula formation between intestine and skin. Some of them are as follows:
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Cancer
- Adhesional lysis
- In addition to these causes, the person who have already faced radiation therapy is susceptible to enterocutaneous fistula.
- Breakdown of anastomotic link, sepsis and enterotomy with trauma are considered the most common predisposing factors of enterocutaneous fistula.
- Perforated peptic ulcer.
- Any kind of injury like a gunshot or stabbing.
- Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
These are the most common symptoms reported regarding enterocutaneous fistula. But this can also occur secondary to an inappropriate surgery.
Enterocutaneous fistula Symptoms
The most common symptoms associated with enterocutaneous fistula are as follows:
- Contents of stomach and intestine start getting leak from the abdominal opening of fistula. And as a result of this, dehydration can occur.
- Diarrhea is also seen in this condition.
- Malnutrition may occur because the nutrients loss due to this fistula leakage.
- Patient can’t eat properly because the content leak through the fistula opening. So the patient feel starvation most of the time.
- Weakness in the lower part of body.
- Fever may also occur due to the invasive organism via fistula opening.
Enterocutaneous fistula Classification
Enterocutaneous fistula is classified into two main classes
- External fistula (Fistula whose outer opening can be seen)
- Internal fistula (the fistula formation between two hollow viscera)
Enterocutaneous fistula is further classified into three groups on the basis of output volume.
- Low output fistula: in which less than 200 ml per day leakage occurs through fistula opening.
- Moderate output fistula: in which 200 to 500 ml per day leakage occurs through fistula opening.
- High output fistula: in which more than 500 ml per day leakage occurs through fistula opening and it is worst state considered and can prove fatal for the patient.
Enterocutaneous fistula Complications
Complications associated with enterocutaneous fistula are sepsis, electrolyte abnormalities and malnutrition. The extent of sepsis occurred totally depends upon the condition of enterocutaneous fistula. As if the fistula formed is direct then the sepsis will also less, but if the fistula formed indirectly with skin then the sepsis rate will be high as well. And the patient may become toxic. Patient may feel ill due to excessive loss of nutrients through leakage via fistula opening. This leakage also cause imbalance in the electrolyte concentration which may prove fatal for the patient.
Enterocutaneous fistula Treatment
Treatment of Enterocutaneous fistula mainly depends upon surgery because membrane rupture can only be corrected via surgery. However, it may triggered due to some kind of underlying infection or pathological state so, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are also used along with surgical intervention.
Enterocutaneous fistula Symptoms, Causes, Calssification, Complications, Treatment
 Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
April 24, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
April 24, 2017
Rating:
 Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
April 24, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Simon Albert
on
April 24, 2017
Rating:











